
Student loan refinance is one of the most effective financial tools available to borrowers today. With more than 45 million Americans currently holding student loan debt, many people look for ways to reduce monthly payments, secure lower interest rates, or pay off their balances faster.
In 2026, interest rates continue to shift, private lenders are becoming more competitive, and many borrowers—especially those with private loans—are choosing refinancing to save money.
This guide covers everything you need to know, including:
- Best refinance lenders
- Available rates and loan terms
- Qualification requirements
- Whether federal borrowers should refinance
- When refinancing becomes a bad idea
- Alternatives such as bankruptcy, settlement, and hardship relief
- Step-by-step refinance process
What Is Student Loan Refinancing?
Student loan refinancing means taking out a new private loan to pay off your existing student loans—federal, private, or both.
The new loan comes with:
- A different interest rate
- New repayment terms
- A new private lender
How Student Loans Work (Before Refinancing)
Most borrowers have multiple loans, each with different interest rates and due dates. Understanding how your current loans work makes it easier to evaluate refinance options.
To learn more, check:
👉 How student loans are collected
👉 Student loan (Wikipedia)
Federal vs Private Loans: Know the Difference Before Refinancing

This distinction is crucial because refinancing federal loans permanently removes federal protections.
Read this comparison:
👉 Federal vs private student loans
Federal Loans Offer:
- Income-driven repayment (IDR)
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
- Hardship deferment
- Forbearance
- Interest waivers during emergencies
Private Loans Offer:
- Higher interest rates
- No forgiveness programs
- Limited hardship relief
Should You Refinance Federal Loans?
Refinancing federal loans converts them into private loans. As a result, you lose:
- PSLF eligibility
- IDR forgiveness
- Hardship protections
- Subsidized interest
- Temporary emergency relief
If you’re experiencing hardship or medical issues, consider:
👉 Student loan relief due to illness
And if repayment feels overwhelming, compare:
👉 Income-driven repayment vs bankruptcy
When Not to Refinance Federal Loans
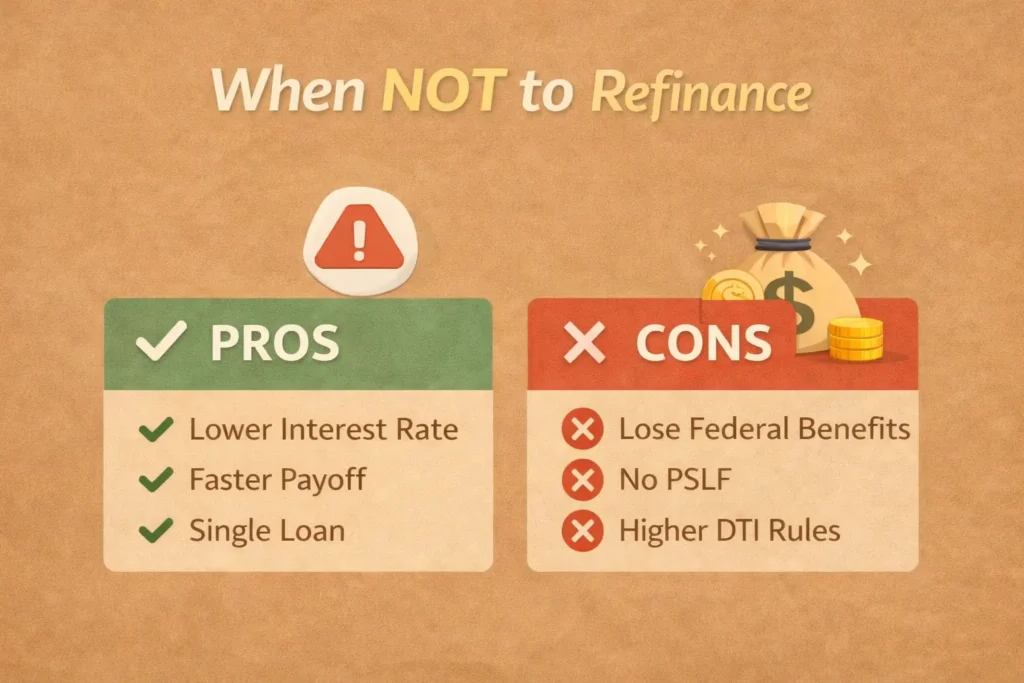
Avoid refinancing federal loans if:
- You want PSLF or IDR forgiveness
- You expect upcoming policy changes
- You need unemployment or hardship support
- Your job stability is uncertain
- Your income is currently low
Refinancing permanently removes federal protections, so choose carefully.
Private Student Loan Refinance: Best Candidates
Refinancing private loans is usually a smart financial move because private loans offer:
- No forgiveness
- Limited relief
- Higher interest rates
Therefore, refinancing is often the best way to reduce monthly payments and save on interest.
If the balance feels overwhelming, explore:
👉 Private student loan settlement
Who Qualifies for Student Loan Refinance?
Typical requirements include:
✔ Credit score 650+
✔ Best rates at 720+
✔ Minimum income: $35,000+
✔ DTI below 40–45%
✔ Full-time employment
✔ Loans not in default
If your loans are in default, consider:
👉 Student loan bankruptcy process step-by-step
Or deeper legal help:
👉 How to file an adversary proceeding
Why Credit Score Matters
Higher credit scores help you secure:
- Lower interest rates
- More lender options
- Longer repayment terms
- Reduced monthly payments
Borrowers with scores above 740 qualify for the best refinance rates.
Student Loan Refinance Rates in 2026
Rates depend on:
- Credit score
- Loan type
- Loan term
- Fixed vs variable rates
Typical 2026 Rates
| Type | Rate Range |
|---|---|
| Fixed | 4.30% – 7.99% |
| Variable | 5.10% – 9.25% |
Borrowers with excellent profiles qualify for the lowest tiers.
Best Student Loan Refinance Lenders in 2026
✔ SoFi
✔ Earnest
✔ Credible
✔ Laurel Road
✔ PenFed
✔ ELFI
✔ Discover
Each lender differs by:
- Approval criteria
- Interest rates
- Payment flexibility
- Cosigner policies
- Bonuses
Student Loan Refinance Calculator

A refinance calculator helps you determine:
- New monthly payments
- Total interest savings
- Best loan terms
- Faster payoff options
Most borrowers save between:
👉 $5,000 to $20,000
Refinancing With Bad Credit
You can still qualify by:
- Adding a cosigner
- Increasing income
- Reducing your DTI
- Showing stable employment
If refinancing becomes impossible or too costly, consider:
👉 Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 bankruptcy
Refinancing Without a Cosigner
To qualify without a cosigner, lenders usually require:
- Strong credit (700+)
- Solid, verifiable income
- Low debt-to-income ratio
- Full-time employment
Self-employed borrowers may use tax returns for approval.
Pros and Cons of Refinancing
Pros
- Lower interest rates
- Reduced monthly payments
- Faster payoff timeline
- Consolidated debt
- Improved financial stability
Cons
- Loss of federal protections
- Ineligible for PSLF
- No IDR forgiveness
- Hard credit inquiry
- More private lender restrictions
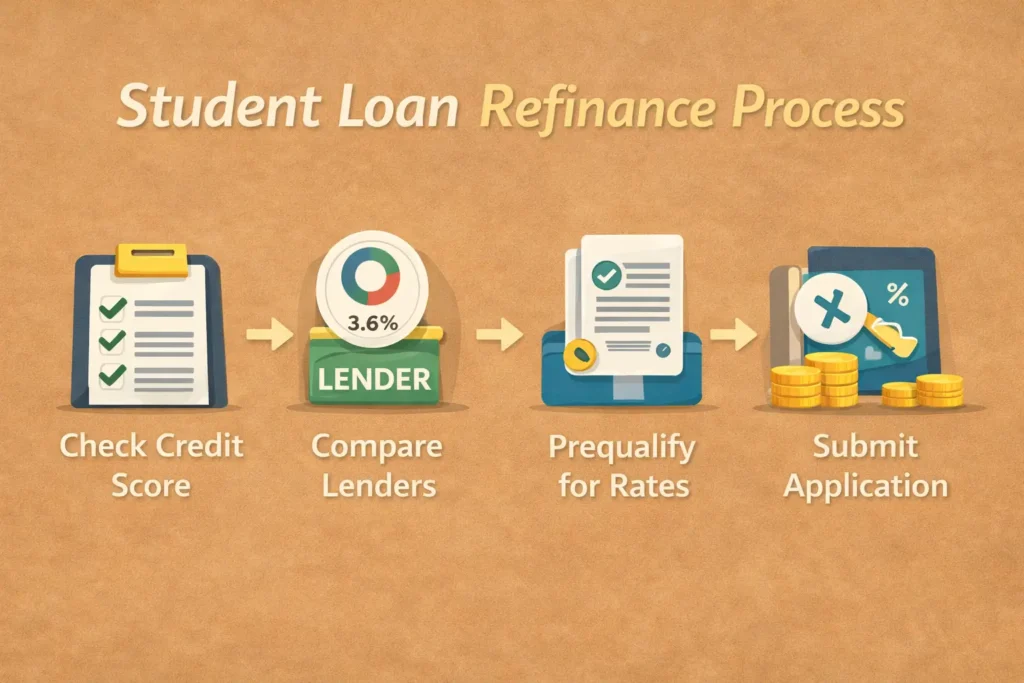
How to Refinance Student Loans (Step-by-Step)
- Check Your Credit Score
Aim for 700+. - Compare Lenders
Use comparison websites. - Prequalify for Rates
Soft inquiry—no score impact. - Select Loan Terms
Fixed or variable, and the loan length. - Submit Your Application
Upload pay stubs, tax returns, and ID. - Wait for Approval
Usually 3–7 business days. - Your Old Loans Get Paid Off
The new lender handles everything.
How Long Does Refinancing Take?
The full process usually takes 1–3 weeks, depending on the lender’s turnaround time and documentation requirements.
Does Refinancing Hurt Your Credit?
There may be a small, temporary impact due to:
- A hard credit inquiry
- A new credit account affecting credit age
However, long-term benefits include:
- On-time payment history
- Lower credit utilization
- Overall score improvement
Refinancing vs Consolidation
| Feature | Refinance | Consolidation |
|---|---|---|
| Lender | Private | Federal |
| Rate | Lower | Weighted average |
| Term | Flexible | 10–30 years |
| Benefits | No federal protections | Retains federal benefits |
Alternatives to Student Loan Refinancing
If refinancing is not the best option, consider:
✔ Income-Driven Repayment (Federal)
- PAYE
- REPAYE
- IBR
- SAVE
✔ Settlement
👉 Private student loan settlement
✔ Bankruptcy
👉 Student loan bankruptcy complete guide
✔ Adversary Proceeding
👉 How to file an adversary proceeding
✔ Hardship Relief
👉 Student loan relief due to illness
Consequences of Not Refinancing
If you keep high-interest loans:
- Interest accumulates faster
- Total debt grows
- Monthly payments rise
- Collections may begin
- Wage garnishment becomes possible
If garnishment already started:
👉 Can bankruptcy stop student loan garnishment?
Final Thoughts: Should You Refinance in 2026?
Refinancing is an excellent choice if:
✔ You have private loans
✔ Your credit score is strong
✔ You want a lower interest rate
✔ You want faster payoff
✔ You want to simplify multiple loans
However, think carefully before refinancing federal loans because federal protections disappear permanently.
Always evaluate IDR, settlement, bankruptcy, or hardship options before making your final decision.















Comments (4)
Best Ways to Lower Student Loan Interest Rates
[…] 👉 Complete refinancing resource:Student Loan Refinance Guide […]
Student Loan Social Security Garnishment: How It Works
[…] For a complete, expert guide to refinancing vs. consolidation, read:👉 Student Loan Refinance Guide […]
Student Loan Help Guide: Lower Payments, Relief & Forgiveness
[…] Learn more through this detailed student loan refinance guide:https://federalstudentloandebt.com/student-loan-refinance-guide/ […]
Subsidized vs Unsubsidized Student Loans - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] If refinancing is an option, review this detailed student loan refinance guide. […]