
Introduction: Why Student Loan Interest Rates Matter More Than Ever
Student loan interest rates impact everything—your monthly payment, your total repayment cost, your ability to refinance, and even your long-term financial goals. Whether you’re taking out new loans, managing existing ones, or planning to refinance, understanding interest rates is the first step to saving money and avoiding unnecessary debt.
In 2026, student loan borrowers face a changing lending environment. Federal interest rates have increased from pre-2020 levels, private lenders are competing aggressively, and many borrowers are seeking ways to reduce their costs through refinancing, repayment plans, and forgiveness programs.
This guide explains everything you need to know about student loan interest rates—how they work, how they are calculated, how to lower them, and how to choose between federal vs private loans. We will also include internal expert resources, such as guides on student loan refinancing, loan collection, and relief during illness, for deeper support.

1. What Are Student Loan Interest Rates?
Student loan interest rates are the percentage you pay to borrow money for your education. They determine how much your debt grows over time and how much you will ultimately repay.
1.1 Definition
An interest rate is the cost of borrowing money. When you take out a student loan, you agree to pay back the original amount (principal) plus interest that accumulates over time.
Example:
If you borrow $20,000 at a 6% interest rate for 10 years, you don’t just repay $20,000—you repay much more over the loan lifetime.
2. Federal vs Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Understanding the difference between federal and private student loans is essential because their interest rate structures are very different. Federal loans offer fixed rates and borrower protections, while private loans vary widely depending on lender risk models.
👉 For an in-depth breakdown, read this:
Federal vs Private Student Loans
2.1 Federal Student Loan Interest Rates
Federal loan rates are set by the U.S. Government each year based on the 10-year Treasury note.
Types of Federal Loans and Rates
- Direct Subsidised Loans: Fixed rates; Government pays interest during school.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: Fixed rates; interest begins immediately.
- PLUS Loans: Higher fixed rates, often for graduate students or parents.
Key Features
✔️ Fixed for life
✔️ No credit check for most federal loans
✔️ Eligible for forgiveness, income-driven plans
2.2 Private Student Loan Interest Rates
Private student loans operate like personal loans or credit cards. Rates depend on:
- Credit score
- Income
- Co-signer strength
- Financial history
- Lender policies
- Variable or fixed rate selection
Rate Types
- Fixed: Same rate for the entire term
- Variable: Changes based on market conditions (may increase your payment)
3. How Student Loan Interest Rates Work
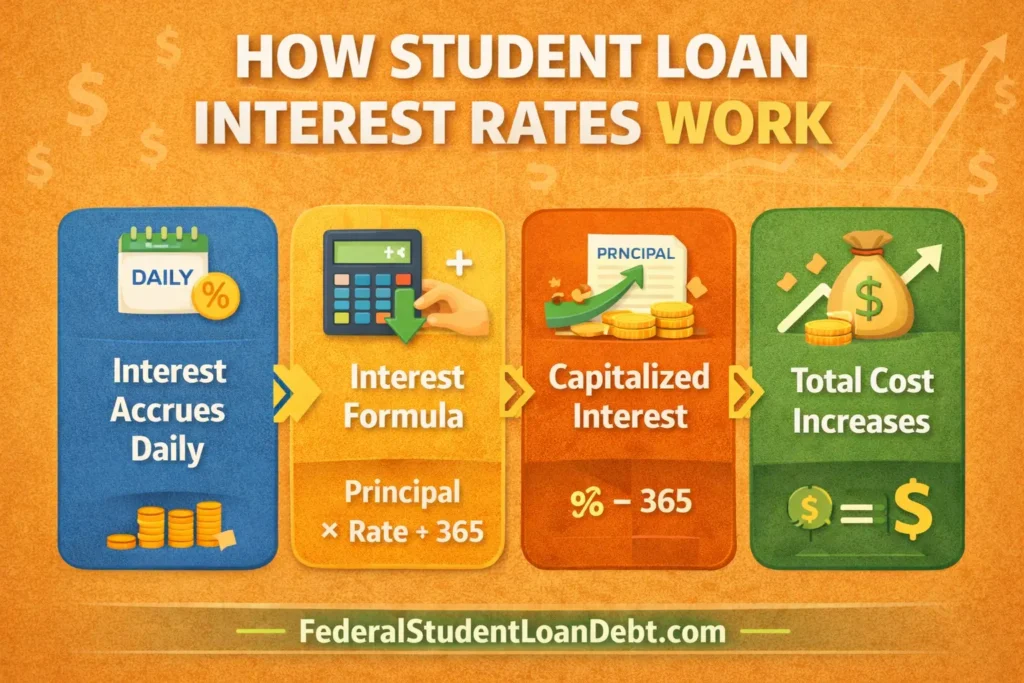
To understand how your loan grows, you must understand daily interest, capitalised interest, and compounding.
3.1 Daily Interest Formula
Private and federal student loans calculate interest daily:
Interest = (Outstanding Principal × Interest Rate ÷ 365)
This means your loan grows every day unless the balance is zero.
3.2 Capitalised Interest
Capitalisation happens when unpaid interest gets added to your loan principal.
This increases your total balance.
Common Times Interest Capitalises:
- After deferment or forbearance
- After you leave school
- When exiting income-driven repayment plans
- When refinancing
Capitalisation can cost borrowers thousands over time.
4. Current Student Loan Interest Rates
Interest rates fluctuate each year, especially federal student loans tied to Treasury notes.
Federal Student Loans 2026 (Approximate Ranges)
- Undergraduate Subsidised/Unsubsidized: 5–6.5%
- Graduate Unsubsidized: 6.5–7.5%
- PLUS Loans: 7.5–8.5%
Private Loan Ranges
- Fixed: 4.5–12%
- Variable: 5–15% (depending on market)
5. Factors That Influence Student Loan Interest Rates
5.1 For Federal Loans
- Treasury note yield
- Government policy
- Education level
5.2 For Private Loans
- Credit score
- Credit history
- Co-signer credit
- Income and debt-to-income ratio
- Lender competition
- Loan term
- Whether you choose fixed or variable rates
6. How to Lower Student Loan Interest Rates
Borrowers often overpay because they don’t take advantage of ways to reduce their interest rates.
Below are the most effective strategies.
6.1 Refinance Your Student Loans
Refinancing can reduce your interest rate by transferring your loan to a private lender with better terms.
👉 Complete refinancing resource:
Student Loan Refinance Guide
You may qualify for:
- Lower fixed rates
- Lower variable rates
- Better repayment terms
Tip: Excellent credit or a strong co-signer helps you get lower rates.
6.2 Set Up Autopay
Most lenders offer a 0.25% reduction for automatic payments.
6.3 Improve Your Credit
Your credit score affects private loan rates and refinancing rates.
Improve credit by:
- Paying bills on time
- Reducing credit utilization
- Removing errors from credit reports
- Avoiding new debt before refinancing
6.4 Choose a Shorter Loan Term
Shorter terms often come with lower interest rates.
6.5 Use Income-Driven Repayment (IDR)
IDR doesn’t lower your interest rate, but it lowers your monthly payments and caps interest.
👉 Compare IDR vs bankruptcy:
Income-Driven Repayment vs Bankruptcy
6.6 Seek Student Loan Relief Programs
If you are struggling due to medical issues, some programs reduce or forgive debt.
👉 Learn more here:
Student Loan Relief Due to Illness
7. Federal vs Private Interest Rates — Which Is Better?
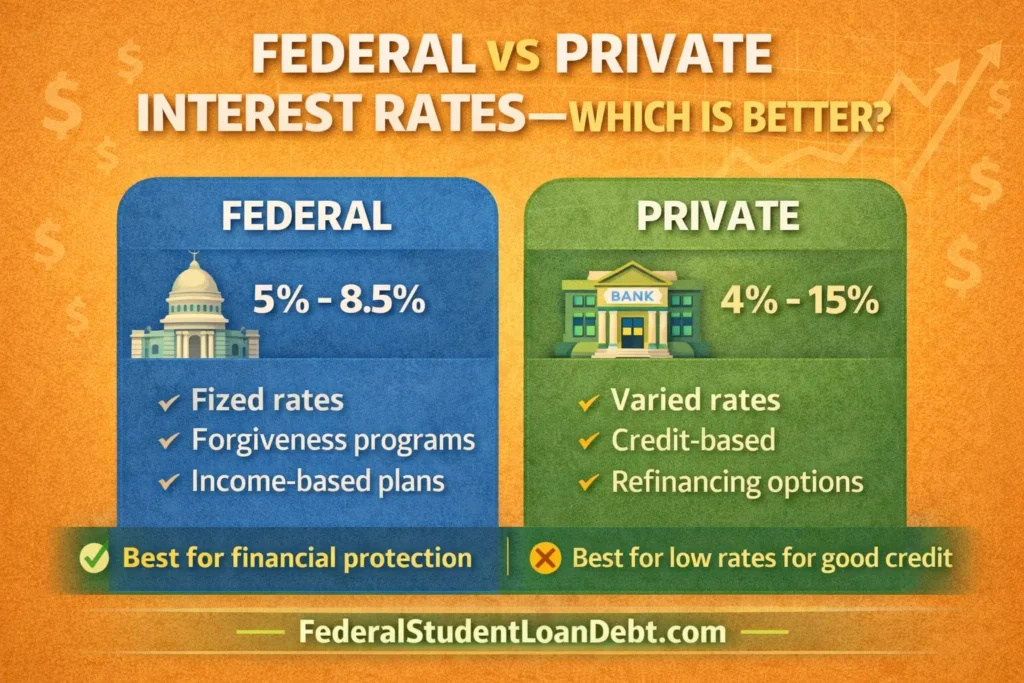
In most cases, federal loans are better for long-term financial protection, while private loans may offer lower initial rates for borrowers with strong credit.
When Federal Is Better
- You need forgiveness programs
- You want stable fixed rates
- You might need a deferment or forbearance
- You have no strong credit history
When Private Is Better
- You have excellent credit
- You want lower variable or fixed rates
- You want to refinance for better terms
8. How Student Loan Interest Rates Affect Your Total Cost
Even a 1–2% difference in interest rates can dramatically change your total financial cost.
Example:
Borrowing $30,000 for 10 years at:
- 4% interest = $36,548 total repayment
- 8% interest = $45,426 total repayment
That’s nearly $9,000 saved with just a 4% difference.
9: Student Loan Interest Rate FAQs
9.1 What is the current student loan interest rate?
Federal rates vary by year, while private lenders set their own. In 2026, federal rates typically range from 5% to 8.5%.
9.2 Are student loan interest rates going up?
Federal rates often increase when Treasury yields rise. Private loan rates may increase based on market conditions, creditworthiness, and lender risk models.
9.3 Can student loan interest rates be reduced?
Yes. You can reduce rates through:
- Refinancing
- Autopay discounts
- Credit score improvement
- Choosing shorter loan terms
- Finding competitive private rates
9.4 How do student loan interest rates work?
Interest accrues daily and is added to your balance. If unpaid, it may capitalize and increase your total cost.
9.5 Why are student loan interest rates high?
Rates are influenced by:
- Market inflation
- Federal Reserve policies
- Treasury note yields
- Lender risk calculations
9.6 Does refinancing lower interest rates?
Often yes. Many refinanced private loans offer significantly lower rates, depending on credit and income.
👉 Read the Student Loan Refinance Guide for full details.
10. How Student Loans Are Collected (Essential for High-Interest Borrowers)
Many borrowers with high interest rates fall behind and end up in collections.
👉 Learn the entire process here:
How Student Loans Are Collected
This guide covers:
- Wage garnishment
- Tax refund seizure
- Social Security offsets
- Collection agency tactics
- How to stop the collection
11. Should You Refinance or Choose Federal Protections?
Borrowers often must choose:
Option A: Lower interest (private)
Option B: Better protections (federal)
Your choice depends on:
- Income stability
- Credit score
- Family situation
- Financial risk tolerance
If you fear job loss or illness, federal protections are safer.
If you have high income and excellent credit, refinancing can save thousands.
12. Summary — How to Choose the Right Student Loan Interest Rate Strategy
Here is a quick summary to help you decide:
Federal loans
✔ Fixed rates
✔ Strong protections
✔ Best for uncertain financial conditions
✔ Eligible for relief programs
Private loans
✔ Potentially lower rates
✔ Credit-based
✔ Best for strong financial profiles
✔ Refinancing available
Conclusion
Student loan interest rates are one of the most important factors in your financial life. Understanding how they work can save you thousands of dollars over your repayment journey. Whether you want to borrow new loans, manage your current ones, or refinance for a better rate, this guide has given you the tools and knowledge to make informed decisions.
Remember:
- Compare federal vs private rates
- Understand how interest accrues
- Explore refinancing options
- Take advantage of borrower protections
- Act early to avoid capitalization and collection
By making smart, strategic decisions now, you can reduce your long-term student loan burden and build a stronger financial future.














