
Student loan wage garnishment can seriously disrupt your financial life. When money is taken directly from your paycheck, managing rent, food, and utilities becomes far more difficult. Under this pressure, many borrowers begin searching for immediate legal solutions.
At that stage, one question usually comes first: Can bankruptcy stop student loan garnishment?
In most situations, the answer is yes—bankruptcy can stop student loan garnishment, and it often works immediately. However, the length and strength of that protection depend on the bankruptcy chapter you file, the type of student loan you owe, and the steps you take after filing.
This guide explains everything in simple terms, so you can clearly understand how bankruptcy affects garnishment and how to protect your income.
How Student Loan Garnishment Begins

Before looking at bankruptcy relief, it helps to understand how student loans are collected.
In most cases, garnishment starts after a borrower defaults on their student loans. At that point, lenders or Government agencies gain powerful collection rights. For example, they may take money from wages or benefits without asking for permission.
Common collection methods include:
- Wage garnishment through your employer
- Federal tax refund offsets
- Social Security benefit offsets
- Court-ordered garnishment for private student loans
Because these rules vary, the way bankruptcy stops garnishment also varies by loan type.
Federal vs Private Student Loan Garnishment
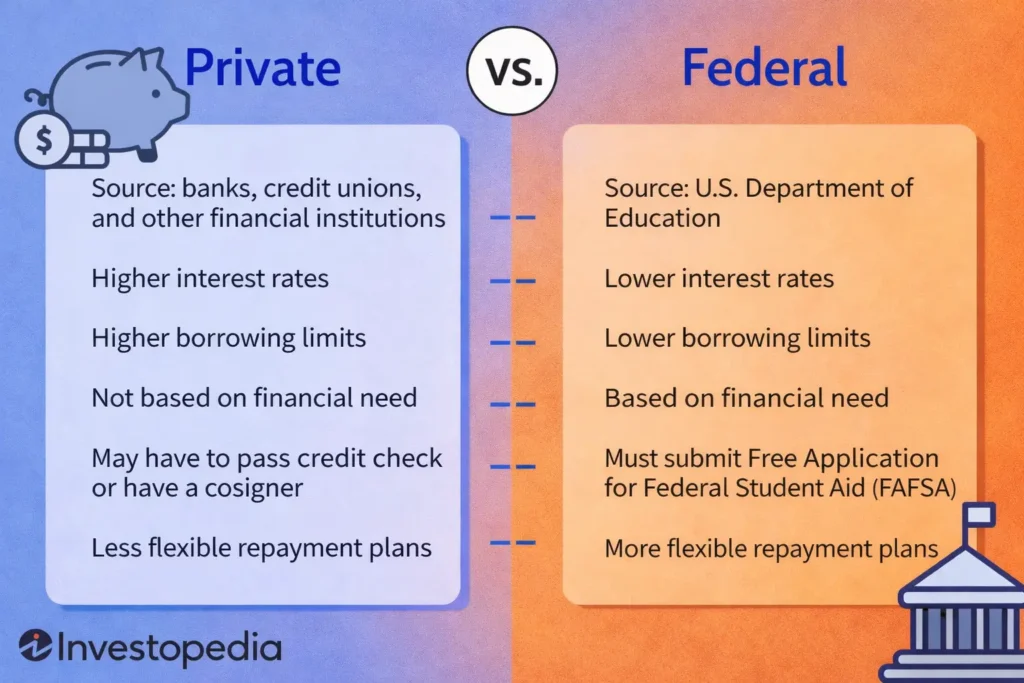
To understand bankruptcy protection, borrowers must first know the difference between federal vs private student loans.
Federal student loans
Federal loans allow the government to collect without filing a lawsuit. As a result, garnishment can begin faster.
- Up to 15% of disposable income may be taken
- Tax refunds and Social Security can be offset
- Bankruptcy still triggers the automatic stay
Private student loans
Private lenders must follow traditional debt laws. Therefore, they must sue you and win before garnishment starts.
- State law limits apply
- Bankruptcy stops lawsuits and judgments
Even though student loans receive special legal treatment, bankruptcy can still interrupt garnishment for both loan types.
Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment?

Yes. Filing for bankruptcy can stop student loan garnishment immediately.
Once you file, the bankruptcy court issues an automatic stay. This legal order forces creditors to stop nearly all collection activity. As a result, wage garnishment must pause.
The automatic stay:
- Stops wage garnishment
- Halts collection lawsuits
- Prevents bank account levies
- Ends collection calls
This protection applies to both federal and private student loans, even though the loans themselves are not automatically discharged.
How the Automatic Stay Protects Your Income
The automatic stay works fast. In most cases, garnishment stops within one payroll cycle.
Here is how the process usually works:
- You file the bankruptcy petition
- The automatic stay takes effect immediately
- Creditors receive legal notice
- Your employer stops withholding wages
However, this protection does not last forever. What happens next depends on whether you choose Chapter 7 or Chapter 13 bankruptcy.
Can Chapter 7 Stop Student Loan Garnishment?
Chapter 7 bankruptcy can stop student loan garnishment, but the relief is usually short-term.
Typically, Chapter 7 cases last three to four months.
During that time, the automatic stay protects your income.
After the case ends, however, garnishment may resume unless further action is taken.
A detailed comparison is available in this guide on Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 bankruptcy for student loans.
What Chapter 7 does
- Stops garnishment quickly
- Discharges most unsecured debts
- Provides fast financial relief
What Chapter 7 does not do
- Discharge student loans automatically
- Offer long-term garnishment protection
Because of these limits, Chapter 7 often works best as a temporary shield.
Can Chapter 13 Stop Student Loan Garnishment?
Unlike Chapter 7, Chapter 13 offers long-term protection against garnishment.
In this chapter, borrowers enter a court-approved repayment plan.
As long as the plan remains active, garnishment stays stopped.
Therefore, many wage earners choose Chapter 13 for stability.
Before filing, it is important to understand the student loan bankruptcy process step by step.
Why Chapter 13 works well
- Garnishment stops immediately
- Protection lasts three to five years
- Monthly payments remain predictable
- Income stability improves

Will Student Loan Garnishment Resume After Bankruptcy?
Student loan garnishment can return, but it does not always happen.
Garnishment may resume if:
- A Chapter 7 case ends with no follow-up action
- A Chapter 13 plan is completed
- Loans remain unresolved
Garnishment may stay stopped if:
- A Chapter 13 plan is still active
- The court discharges the loan
- A settlement or repayment plan is approved
Therefore, long-term relief depends on what steps you take after filing bankruptcy.
Can Bankruptcy Permanently Stop Student Loan Garnishment?
Bankruptcy can permanently stop garnishment only if the student loan itself is resolved.
In most cases, this requires filing an adversary proceeding.
Borrowers should first understand how to file an adversary proceeding before pursuing discharge.
Courts usually review:
- Income compared to basic living expenses
- Long-term financial outlook
- Good-faith repayment efforts
If the court grants a discharge, garnishment ends permanently.
Alternatives to Bankruptcy for Stopping Garnishment
Bankruptcy is powerful, but it is not always the only solution.
In some cases, negotiated solutions work better.
For example, borrowers may explore private student loan settlement options to stop garnishment without filing bankruptcy.
Other alternatives include:
- Federal loan rehabilitation
- Income-driven repayment plans
- Temporary hardship deferment
- Direct lender negotiation
Why Student Loan Garnishment Laws Are So Strict
To fully understand why garnishment rules are aggressive, it helps to review the system of student loans in the United States.
Because federal law treats student loans differently from other debts, borrowers must rely on structured legal solutions instead of quick fixes.
Key Takeaways
- Bankruptcy can stop student loan garnishment
- The automatic stay provides immediate relief
- Chapter 7 offers short-term protection
- Chapter 13 offers long-term protection
- Permanent relief requires additional legal steps
Final Thoughts
Student loan garnishment can overwhelm even responsible borrowers. Fortunately, bankruptcy offers a legal way to stop the damage and regain control. When used correctly, it can protect your income and create space for long-term recovery.















Comments (4)
Student Loan Bankruptcy: Discharge, Relief & Legal Options
[…] Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment→ How Student Loans Are […]
Student Loan Relief Due to Illness: Medical Hardship Options
[…] 👉 Bankruptcy can stop student loan garnishment […]
Student Loan Social Security Garnishment: How It Works
[…] For those wondering whether bankruptcy stops garnishment:👉 Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment? […]
Income Driven Repayment vs Bankruptcy: Which Saves More?
[…] If garnishment is already happening, bankruptcy can provide immediate relief, as explained inCan bankruptcy stop student loan garnishment […]