
Getting a student loan is one of the most important financial decisions you will ever make. Whether you are applying for federal aid, exploring private lenders, or searching for the easiest way to secure funding quickly, knowing the steps, requirements, and strategies will help you avoid common mistakes and ensure approval.
This guide explains how to get a student loan, from filling out the FAFSA to choosing the right lender. It also covers the required documents, eligibility criteria, timelines, tips for approval, and more.
1. Understand the Two Main Types of Student Loans
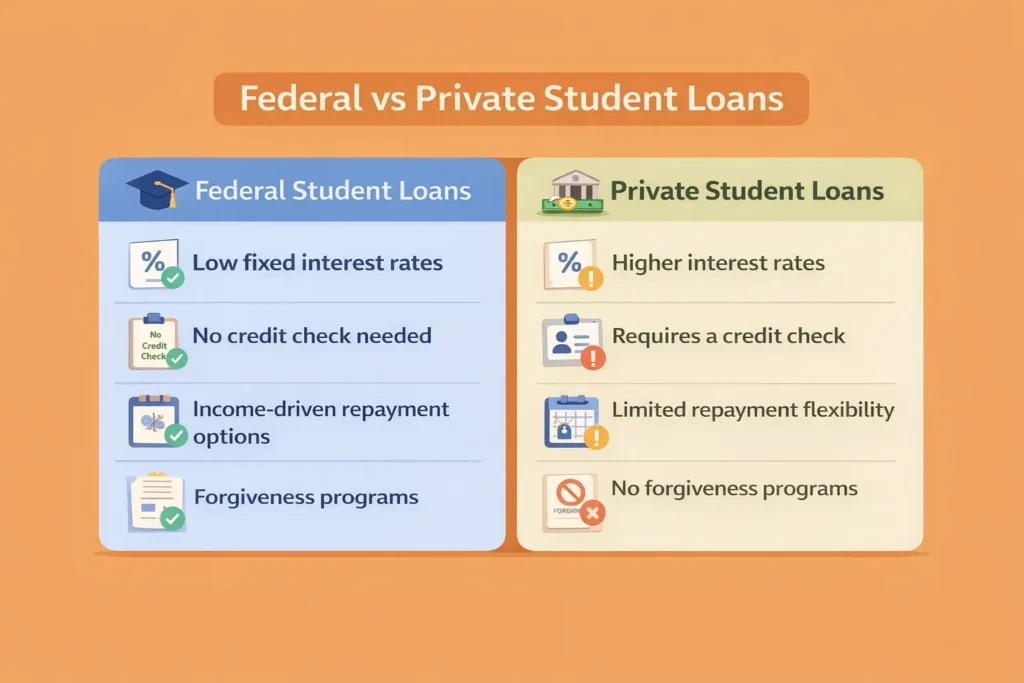
Before applying, you must understand the difference between federal and private student loans. This affects your interest rates, repayment options, eligibility for forgiveness, and the ease of approval.
1.1 Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans are issued by the U.S. Department of Education. They offer:
- Low fixed interest rates
- No credit check (for most loans)
- Income-driven repayment options
- Forgiveness programs
- Flexible deferment options
If you need help comparing loan types, read:
Federal vs Private Student Loans
1.2 Private Student Loans
Private loans come from:
- Banks
- Credit unions
- Online lenders
These typically require:
- A credit check
- A cosigner
- Higher interest rates
But they can fill funding gaps when federal loans are insufficient.
Private loan borrowers often explore settlement options later. Learn more:
Private Student Loan Settlement
2. How to Get a Federal Student Loan
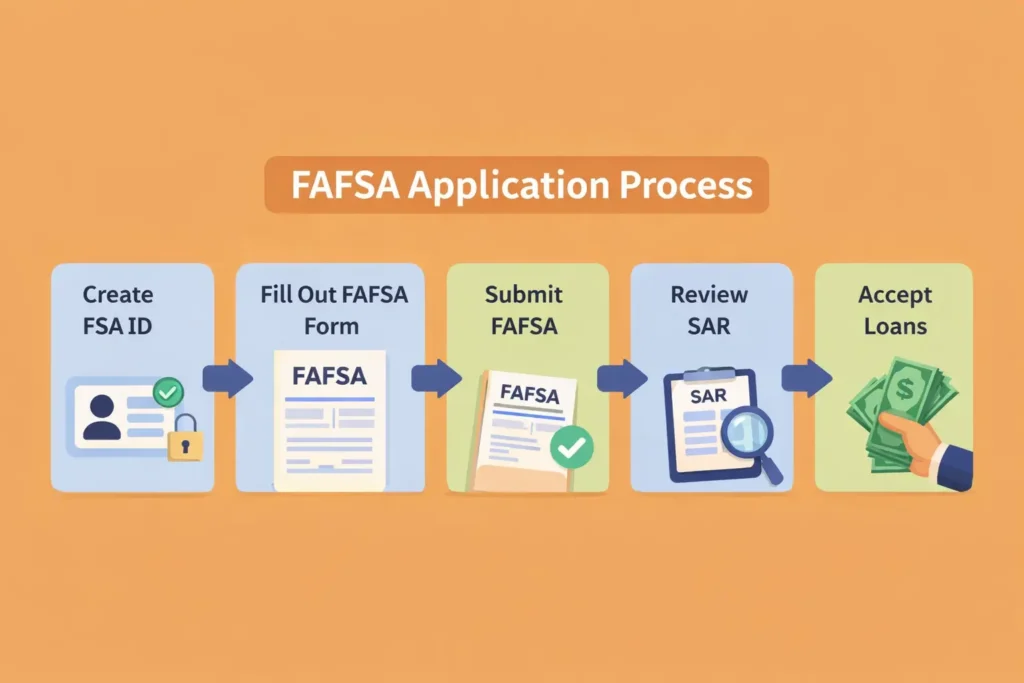
Federal loans are the simplest and most affordable option. Here is the exact process for 2026.
Step 1: Create Your FAFSA Account
Visit studentaid.gov and create an FSA ID.
You will need:
- Social Security number
- Phone number
- Email address
Step 2: Fill Out the FAFSA
The FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) determines your eligibility for:
- Pell Grants
- Federal student loans
- Work-study
- Other institutional aid
Key documents needed:
- Tax returns
- W-2 forms
- Bank statements
- Income records
If you need help comparing post-approval repayment options, see:
Income-Driven Repayment vs Bankruptcy
Step 3: Review Your Student Aid Report (SAR)
Your SAR will summarize:
- Expected Family Contribution
- Pell Grant eligibility
- Federal loan amounts
- Errors you need to correct
Step 4: Accept Your Federal Loans
Your school will send a financial aid package. You can accept:
- Direct Subsidized Loans
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans
- PLUS Loans (for parents or grad students)
Step 5: Complete Entrance Counseling + MPN
The Master Promissory Note is your binding loan contract.
Entrance counseling ensures you understand:
- Your interest rate
- Repayment obligations
- Loan limits
Step 6: Receive Your Loan Disbursement
Funds go directly to your school to cover:
- Tuition
- Fees
- Housing
Excess money is refunded to you.
3. How to Get a Private Student Loan
If federal loans aren’t enough—or you don’t qualify—you may need a private student loan.
Here is how the process works.
3.1 Check Your Credit Score
Most lenders require:
- 650+ credit score
- Low debt-to-income ratio
If your credit is poor, you may still qualify with a cosigner.
3.2 Compare Lenders
Look for lenders with:
- Low APR
- Fixed-rate options
- Flexible repayment terms
Always compare student loan offers before applying.
3.3 Apply Online
You will need:
- ID
- Income proof
- School information
- Cosigner details (if needed)
3.4 Complete Certification With Your School
Your lender confirms your:
- Enrollment status
- Loan amount
- Academic standing
3.5 Receive Your Funding
Just like federal loans, funds go to your school first.
If you later face repayment issues, explore relief options:
Student Loan Relief Due to Illness
4. Student Loan Requirements You Must Meet
Before applying, make sure you meet these requirements.
4.1 Federal Loan Requirements
You must:
- Be a U.S. citizen or eligible noncitizen
- Have a valid Social Security number
- Be enrolled at least half-time
- Maintain satisfactory academic progress
- Not be in default on federal loans
- Complete the FAFSA
4.2 Private Loan Requirements
Private lenders require:
- Good credit
- Stable income
- Cosigner (usually)
- Enrollment in an eligible school
5. Documents Needed to Get a Student Loan
Here are all the required documents for federal and private loans.
For FAFSA
- SSN
- Driver’s license (optional)
- Tax returns
- W-2 forms
- Bank statements
- Investment records
For Private Loans
- Government ID
- Social Security number
- Proof of address
- School acceptance letter
- Pay stubs/income verification
6. How to Get a Student Loan Fast
If you need funding quickly, follow these steps:
6.1 Submit FAFSA Early
Early applicants get faster processing.
6.2 Have All Documents Ready
This reduces delays.
6.3 Choose a Lender With Quick Approval
Many private lenders offer instant prequalification.
6.4 Maintain Good Credit
Higher credit = faster approval.
7. How to Get a Student Loan Without a Cosigner

Not having a cosigner is common. You may still qualify.
7.1 Choose Federal Loans (No Cosigner Needed)
Federal loans never require a cosigner.
7.2 Choose Private Lenders With Non-Cosigner Loans
A few lenders offer no-cosigner student loans for:
- Graduate students
- Medical students
- Law students
7.3 Build Your Credit
Higher credit improves approval odds.
8. How to Get a Student Loan With Bad Credit
Bad credit makes approval harder, but still possible.
8.1 Federal Loans Don’t Check Credit
Except for PLUS loans.
8.2 Use a Cosigner
Increases approval chances dramatically.
8.3 Compare Lenders for Bad-Credit Loans
Some lenders specialize in low-credit borrowers.
8.4 Improve Credit Before Applying
Pay off small debts
Reduce credit utilization
Correct errors on your credit report
9. How Much Student Loan Can You Get?
Federal loan limits depend on:
- Grade level
- Dependency status
- Subsidized vs unsubsidized eligibility
Annual Federal Loan Limits
- Dependent freshmen: $5,500
- Independent freshmen: $9,500
- Undergraduates: Up to $12,500/year
- Graduate students: Up to $20,500/year
Private loans typically allow up to the full cost of attendance.
10. Timeline: How Long Does It Take to Get a Student Loan?
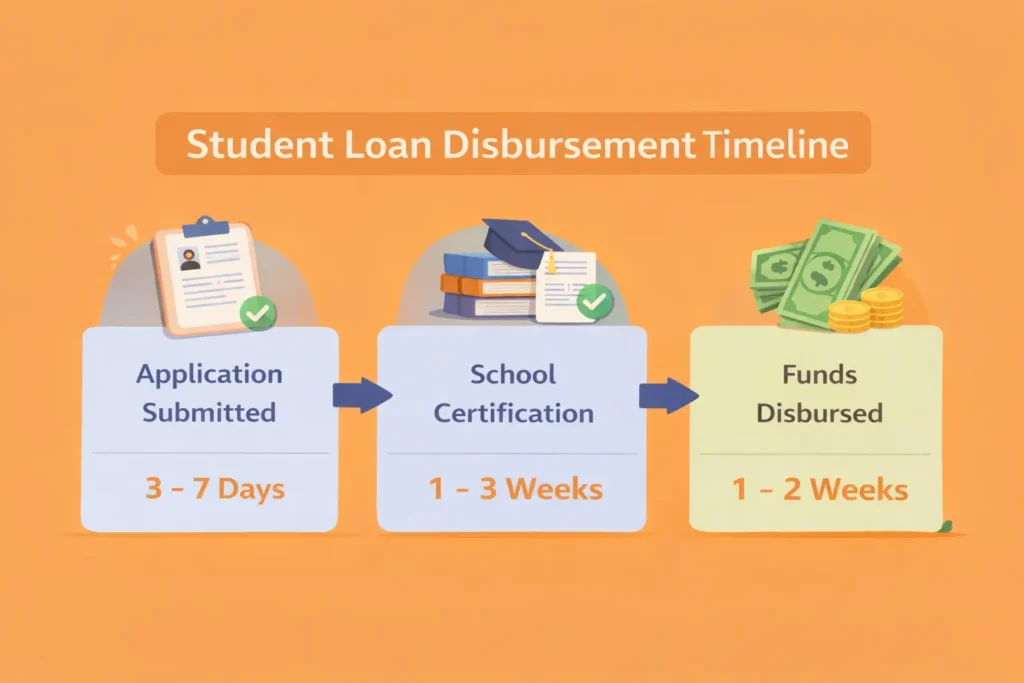
FAFSA Loans
- Processing: 3–5 days
- Aid package: 1–3 weeks
- Disbursement: Start of semester
Private Loans
- Prequalification: Minutes
- Full approval: 2–7 days
- Disbursement: 1–3 weeks
11. Mistakes to Avoid When Applying for Student Loans
- Waiting too long to complete FAFSA
- Borrowing more than needed
- Ignoring interest rate differences
- Not comparing lenders
- Not understanding repayment options
- Not checking the credit before applying
If payments become difficult later, explore discharge options:
Student Loan Bankruptcy Guide
Also see the full step-by-step breakdown:
Student Loan Bankruptcy Process
Some borrowers also explore:
Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy
12. How Interest Rates Work for Student Loans
Federal Loans
Rates are set each year and fixed.
Private Loans
Rates depend on:
- APR
- Credit score
- Variable or fixed options
- Market conditions
Comparing lenders matters. If refinancing later:
Student Loan Refinance Guide
13. Repayment Options After Getting a Loan
Federal loans offer:
- Standard repayment
- Graduated repayment
- Extended repayment
- Income-driven repayment
Income-driven plans include:
- SAVE plan
- PAYE
- REPAYE (older version)
- IBR
If you fall behind, read:
How Student Loans Are Collected
If your wages are being garnished, see:
Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment?
14. What to Do If Denied for a Student Loan
Here are options:
- Add a cosigner
- Improve credit
- Apply for federal loans
- Choose a school with lower tuition
- Explore income-driven repayment if struggling later
- Appeal the school’s decision
15. People Also Ask
How do I qualify for a student loan?
You need to complete the FAFSA to qualify for federal loans. Private loans require good credit, income, and sometimes a cosigner.
What documents do I need?
Tax returns, ID, income records, school information, and credit details for private loans.
Can I get a student loan without parents?
Yes. Federal loans do not require parents. Private lenders may require a cosigner if your credit is low.
Can I get a student loan fast?
Yes. Private lenders offer quick prequalification. FAFSA should be completed early for the fastest approval.
Can I get a student loan with bad credit?
Yes. Federal loans allow it. Private loans require a cosigner or improved credit.
How much can I borrow?
Undergraduates can borrow up to $12,500 per year from the federal Government. Private loans can cover the full cost of attendance.
Do I need credit for FAFSA?
No. Federal loans do not require credit checks (except PLUS loans).
16. Choose Loans Carefully
Student loans can help you complete your degree, but borrowing wisely is essential. Always begin with federal loans, compare lenders, understand repayment plans, and avoid borrowing more than needed.
If you ever face financial hardship later in life, explore forgiveness, settlement, refinancing, or bankruptcy options using the internal resources linked in this guide.















1 Comment
Best Student Loan Refinance Companies - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] you are new to borrowing, this guide to getting a student loan explains the basics in […]