
Quick Summary
- Student loans (education loans) help students pay for tuition, housing, books, and living costs
- Federal and private student loans work very differently in terms of interest, repayment, and forgiveness
- Interest, repayment plans, and long loan terms explain why student loans grow so fast
- Choosing the right loan type early can save thousands of dollars later
- Understanding repayment options is as important as choosing the loan itself
What Is a Student Loan or Education Loan?
A student loan (also called an education loan) is borrowed money used to pay for higher education expenses, which must be repaid with interest after or during studies.
Student loans are offered by governments, banks, and private lenders, each with different rules, interest rates, and repayment protections.
What exactly is a student loan, and how does it work?
A student loan provides upfront funds for education, repaid later in monthly installments with interest.
A student loan covers:
- Tuition fees
- Hostel or housing costs
- Books, laptops, and supplies
- Daily living expenses
After graduation (or leaving school), repayment begins based on the loan’s terms.
To understand why balances rise over time, see why student loans grow so quickly in the United States.
Student loans delay education costs today but shift repayment pressure to your future income.
Types of Student Loans Explained (Federal vs Private)
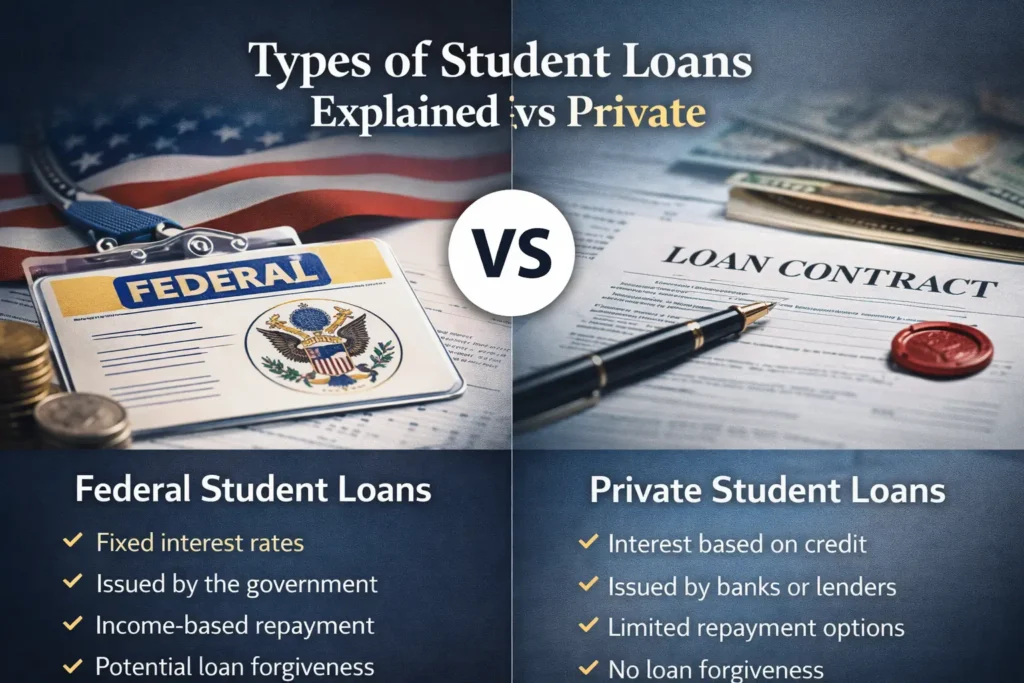
Student loans fall into two main categories: federal and private.
Federal Student Loans
- Issued by the government
- Fixed interest rates
- Income-driven repayment options
- Possible loan forgiveness
Private Student Loans
- Issued by banks or private lenders
- Interest based on credit score
- Limited repayment flexibility
- No forgiveness programs
A detailed breakdown is available in the federal vs private student loans.
Federal loans prioritize borrower protection; private loans prioritize lender profit.
How much can you borrow with an education loan?
Borrowing limits depend on loan type, education level, and country regulations.
In the United States (USD):
- Federal loans have annual and lifetime caps
- Graduate students can borrow more than undergraduates
- Private loans may cover up to the full cost of attendance
In countries like Canada, the UK, and Australia, limits depend on tuition caps and residency status.
Loan limits protect students from over-borrowing—but private loans can bypass those limits.
How does student loan interest actually work?
Student loan interest is the cost lenders charge for borrowing money, calculated annually.
Interest types:
- Fixed interest: stays the same
- Variable interest: changes with market rates
Interest may accrue:
- During school
- During grace periods
- During deferment (private loans)
Learn the mechanics of how student loan interest works.
Interest accumulation—not borrowing alone—is what makes student loans expensive.
Why do student loans grow so fast over time?
Student loans grow due to compound interest, long repayment terms, and delayed payments.
Key reasons:
- Interest capitalization
- Low early-career income
- Extended repayment plans
- Missed or deferred payments
This problem is analyzed in depth in Why Student Loans Grow So Quickly in the United States.
Time + interest = debt growth, even without new borrowing.
What repayment options are available after graduation?
Borrowers can choose standard, extended, graduated, or income-driven repayment plans.
Popular repayment options:
- Standard 10-year repayment
- Income-Driven Repayment (IDR)
- Extended or graduated plans
A full explanation is available in the “Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) Plans” section.
The right repayment plan can reduce monthly stress—even if total cost increases.
Can student loans be forgiven or canceled?
Some federal student loans qualify for forgiveness after long-term repayment or public service.
Forgiveness paths include:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
- Income-driven forgiveness (20–25 years)
- Disability or school closure discharge
Private student loans rarely qualify.
Loan forgiveness exists—but only for specific federal borrowers.
Student Loan Consolidation vs Refinancing: What’s the difference?
Consolidation combines loans; refinancing replaces loans with a new private lender.
| Feature | Consolidation | Refinancing |
| Keeps federal benefits | ✅ | ❌ |
| Changes the interest rate | ❌ | ✅ |
| Credit check required | ❌ | ✅ |
Borrowers struggling with private debt may explore private student loan debt settlement.
Refinancing saves money; consolidation preserves protections.
Is taking an education loan worth it?
Education loans can be worth it if future income justifies long-term repayment.
Ask yourself:
- Will this degree increase earning potential?
- Are scholarships or grants available?
- Is the loan federal or private?
For guidance, explore student loan help resources.
A student loan is an investment—only if returns exceed costs.
Common Student Loan Mistakes to Avoid
Most borrowers over-borrow and under-understand repayment terms.
Mistakes include:
- Ignoring interest accumulation
- Choosing private loans first
- Missing grace period planning
- Not contacting lenders early
If you need personalized guidance, visit our contact page.
Knowledge saves more money than negotiation later.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between a student loan and an education loan?
They mean the same thing; “education loan” is commonly used outside the US.
Are student loans bad debt?
They are considered “good debt” only if income growth follows graduation.
Can parents take out education loans?
Yes, Parent PLUS and private parent loans are available.
What happens if I can’t repay my student loan?
Options include deferment, income-based repayment, or settlement, depending on the loan type.
Where can I learn more about student loans?
A general overview is available according to this student loan explanation on Wikipedia.
What matters most
Student loans are powerful tools—but dangerous if misunderstood.
The smartest borrowers focus less on “getting the loan” and more on repayment strategy before borrowing.














