
Choosing the correct type of student loan can affect your finances for decades. Because of this, one of the most common and essential questions borrowers ask is: federal vs private student loans—what’s the difference, and which is better?
Both options help pay for college. However, they operate under very different rules—especially when you understand how student loans are collected and what happens if payments are missed.
From interest rates and repayment options to forgiveness programs and borrower protections, the gap between federal and private student loans is significant.
In this in-depth guide, we explain the difference between federal and private student loans, compare their pros and cons, and help you decide which student loan is better for your situation.
What Are Federal Student Loans?
Federal student loans are education loans funded by the U.S. Department of Education. Their primary purpose is to make higher education accessible, especially for students with financial need.
As a result, federal student loans come with fixed interest rates, standardized repayment plans, and strong legal protections that private lenders do not offer.
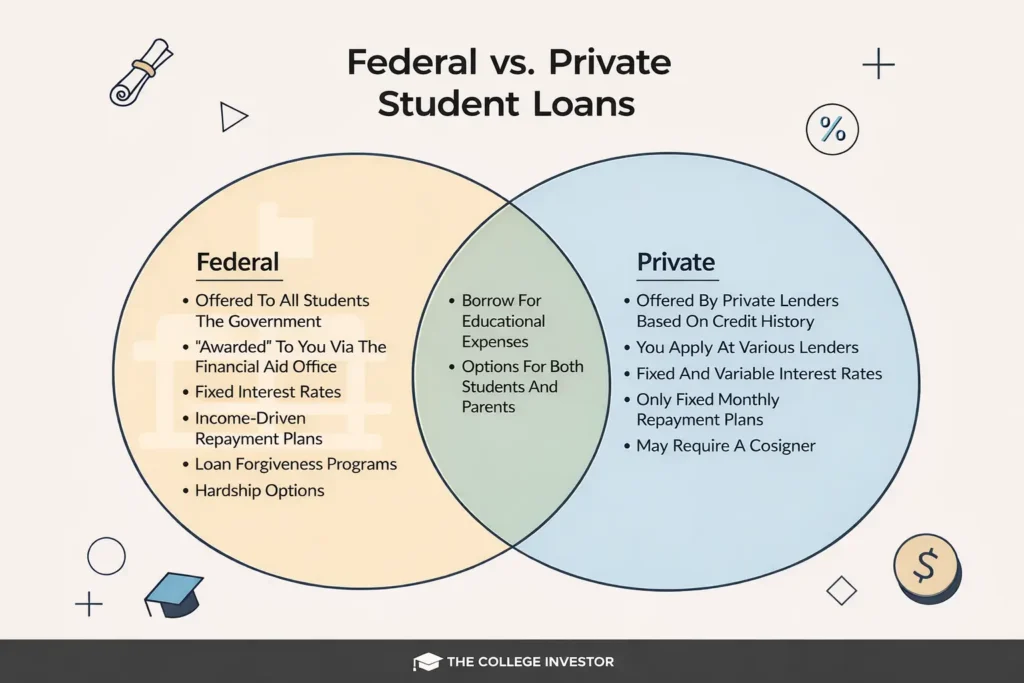
Common Types of Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans generally fall into the following categories:
- Direct Subsidized Loans – The Government pays interest while you’re in school
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans – Interest accrues immediately
- Direct PLUS Loans – For graduate students and parents
- Direct Consolidation Loans – Combine multiple federal loans into one
What Are Private Student Loans?
Private student loans, as defined in a widely cited overview of private student lending in the United States, are issued by banks, credit unions, and online lenders rather than the federal Government.
Instead of financial need, approval is based on credit history, income, and debt-to-income ratio.
In many cases, private loans help fill the gap when federal aid is not enough. However, they typically offer fewer borrower protections and less flexibility.
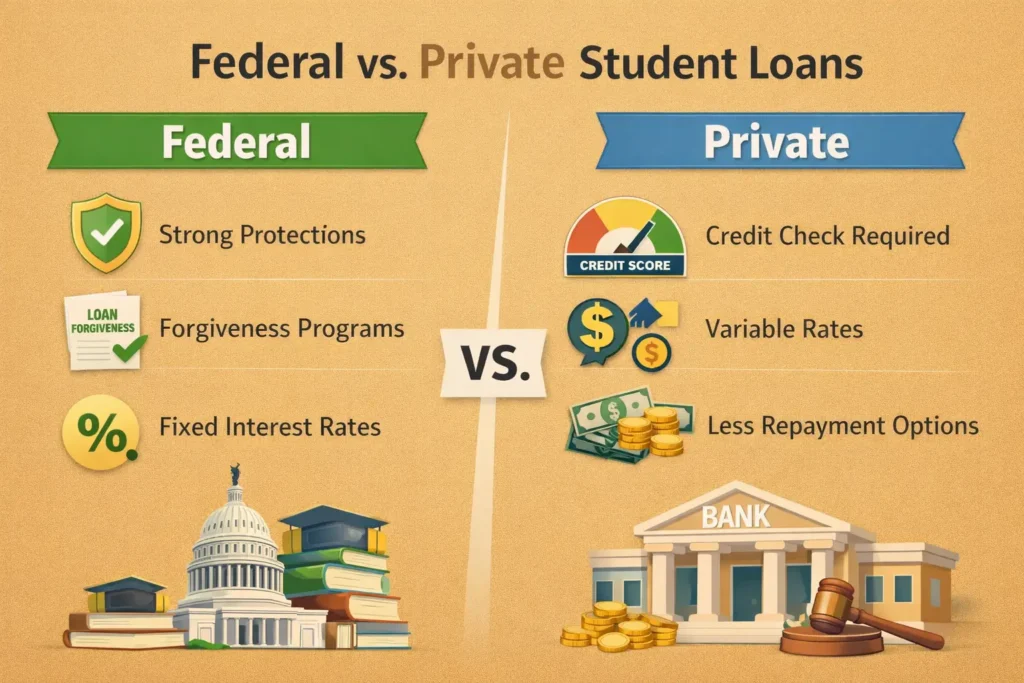
Federal vs Private Student Loans: Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | Federal Student Loans | Private Student Loans |
| Interest Rates | Fixed, set by law | Fixed or variable |
| Credit Check | Not required (most loans) | Required |
| Repayment Options | Income-driven plans available | Limited options |
| Loan Forgiveness | Yes (PSLF, IDR) | Rare |
| Deferment & Forbearance | Broad protections | Lender-specific |
| Bankruptcy Relief | Possible with hardship | Very limited |
The Difference Between Federal and Private Student Loans Explained
1. Eligibility Requirements
Federal student loan eligibility is based primarily on:
- FAFSA submission
- Enrollment status
- Financial need (for subsidized loans)
Importantly, no credit check is required for most federal loans.
Private student loan eligibility, on the other hand, depends on:
- Credit score
- Income level
- Employment history
- Co-signer availability
Because of this, private loans are harder to qualify for—especially for students without established credit.

Federal Student Loans vs Private Loans: Interest Rates Compared
Interest rates are among the most searched topics when comparing federal vs private student loans.
Federal Student Loans
- Fixed interest rates
- Same rate for all borrowers in the same program
- Rates set annually by Congress
Private Student Loans
- Fixed or variable rates
- Rates vary by lender and borrower credit
- Variable rates can increase significantly over time
💡 Important: A low starting rate on a private loan may become much higher over the life of the loan.
Federal vs Private Student Loans Repayment Options
Federal Student Loans Repayment Options
Federal loans offer flexible, borrower-friendly repayment plans, including:
- Standard Repayment (10 years)
- Graduated Repayment
- Extended Repayment
- Income-Driven Repayment (IDR) plans:
- PAYE
- REPAYE
- IBR
- ICR
If repayment becomes difficult, federal borrowers often have structured relief options before severe consequences occur.
Private Student Loan Repayment Options
Private lenders typically offer:
- Fixed monthly payments
- Limited hardship options
- Short forbearance periods (if any)
Unlike federal loans, income-based repayment is not guaranteed.
Because private lenders offer fewer protections, some borrowers explore private student loan settlement options to avoid aggressive collections or lawsuits.
Federal vs. Private Student Loans: Pros and Cons
Federal Student Loans – Pros
- No credit check required
- Fixed interest rates
- Income-driven repayment plans
- Loan forgiveness programs
- Strong borrower protections
- Easier deferment and forbearance
Federal Student Loans – Cons
- Annual borrowing limits
- Slower processing
- Less flexibility for major expenses
Private Student Loans – Pros
- Higher borrowing limits
- Faster approval
- Competitive rates for excellent credit borrowers
Private Student Loans – Cons
- Credit-based approval
- Fewer repayment options
- No guaranteed forgiveness
- Limited hardship protections
Federal vs. Private Student Loan Forgiveness Programs
Federal Student Loan Forgiveness
Federal loans may qualify for:
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF)
- Income-Driven Repayment forgiveness (20–25 years)
- Teacher Loan Forgiveness
- Total and Permanent Disability discharge
In some cases, these programs can eliminate thousands—or even hundreds of thousands—of dollars in debt.
Private Student Loan Forgiveness
Private student loans do not offer standardized forgiveness programs. Any forgiveness, if available, is entirely at the lender’s discretion and extremely rare.
Are Federal or Private Student Loans Better?
For most borrowers, federal student loans are better because they:
- It is easier to qualify for
- Offer flexible repayment
- Include forgiveness and legal protections
Private student loans may be better only if:
- You’ve maxed out federal loans
- You have excellent credit
- You fully understand and accept the risks
What Happens If You Can’t Pay?
If repayment becomes impossible, options differ sharply.
Federal borrowers may explore income-driven repayment, consolidation, or legal relief through filing an adversary proceeding in bankruptcy.
Private loan borrowers, by contrast, often face aggressive collections, lawsuits, and wage garnishment.
Federal vs Private Student Loans and Bankruptcy
Both federal and private student loans are difficult—but not impossible—to discharge.
To understand eligibility rules, hardship standards, and court procedures, review this complete guide to student loan bankruptcy relief.
Final Verdict: Federal vs Private Student Loans
In conclusion, federal student loans should almost always be your first choice.
They provide unmatched flexibility, forgiveness opportunities, and borrower protections.
Private student loans should be used only as a supplement, not a replacement.















Comments (24)
Student Loan Bankruptcy: Discharge, Relief & Legal Options
[…] Private Student Loan Settlement OptionsFederal vs Private Student Loans […]
Private Student Loan Settlement Options Explained
[…] Private Student Loan Settlement Impact on Credit […]
How to File an Adversary Proceeding in Bankruptcy Court
[…] Understanding the difference between federal and private student loans is essential before […]
How Student Loans Are Collected | Federal vs Private Loans
[…] ➡️ Federal vs. Private Student Loans: How Collection Rules Differ […]
Student Loan Bankruptcy Process Step by Step
[…] ➡️ Federal vs. Private Student Loans: Legal Differences Borrowers Must Know […]
Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment? Explained
[…] To understand bankruptcy protection, borrowers must first know the difference between federal vs private student loans. […]
Income Driven Repayment vs Bankruptcy: Which Is Better for Student Loans?
[…] IDR applies only to federal loans, understanding the difference between federal and private student loans is critical before relying on this […]
Medical Hardship Student Loan Relief: Forgiveness, Discharge, and Legal Options Explained - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] 👉 federal vs private student loans […]
Student Loan Relief Due to Illness: Medical Hardship Options
[…] 👉 federal vs private student loans […]
Student Loan Consolidation Guide 2026
[…] For a deeper understanding of loan categories, check:👉 Federal vs private student loans […]
Student Loan Social Security Garnishment: How It Works
[…] If you need clarity on the different types of student loans, read:👉 Federal vs Private Student Loans […]
Best Ways to Lower Student Loan Interest Rates
[…] 👉 For an in-depth breakdown, read this:Federal vs Private Student Loans […]
How to Get a Student Loan in 2026 | Complete Step-by-Step Guide
[…] If you need help comparing loan types, read:Federal vs Private Student Loans […]
Student Loan Refinance: How It Works, Best Lenders
[…] Read this comparison:👉 Federal vs private student loans […]
Student Loan Forgiveness for Teachers
[…] 👉 federal vs private student loans […]
Federal Student Loan Forgiveness Public Service Application
[…] Understand the difference between federal and private student loans […]
Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy for Student Loans
[…] addition, learning the legal differences between federal vs private student loans can help you choose the right debt relief […]
Student Loan Help Guide: Lower Payments, Relief & Forgiveness
[…] Before choosing the right type of student loan help, you must know whether your loans are federal or private. Each has different relief options.You can learn more in this guide on federal vs private student loans:https://federalstudentloandebt.com/federal-vs-private-student-loans/ […]
Student Loan Deferment Guide 2026: Eligibility, Hardship & Steps
[…] To understand differences, see this comparison:👉 Federal vs Private Student Loans […]
What Is a Student Loan? Full Guide to Types, Rates & Repayment
[…] Private lenders charge higher interest and offer fewer protections.A complete comparison of federal vs private student loans is available here:👉 https://federalstudentloandebt.com/federal-vs-private-student-loans/ […]
Student Loan Payment Plan: Complete Guide to Repayment Options, Forgiveness, Interest, and Strategies - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] Others compare loan types before selecting a plan. If you are unsure whether your loans are federal or private, this comparison helps:👉 Federal vs private student loans comparison […]
Student Loan Forgiveness Programs: The Complete 2026 Guide to Eligibility, Types, Applications & Legal Relief Options Student Loan Forgiveness Programs: Eligibility, Types & Relief Guide - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt
[…] If you’re unsure whether your loans are federal or private, use this comparison guide:👉 Federal vs Private Student Loans – Full Comparisonhttps://federalstudentloandebt.com/federal-vs-private-student-loans/ […]
Student Loan Debt Help: Relief, Forgiveness & Repayment Options Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] To understand the difference, see:👉 Federal vs private student loans comparison […]
Is Student Loan Bankruptcy Worth It? Pros & Cons Explained
[…] You can check your loan category using:✔ federal vs private student loans […]