
Filing bankruptcy can eliminate or reorganize many debts, but some disputes require more than a simple motion. If you are dealing with student loan discharge, creditor fraud, lien disputes, or challenges to debt dischargeability, you may need to take an additional legal step—filing an adversary proceeding.
This in-depth guide explains how to file an adversary proceeding, when it is required, the exact filing steps, deadlines, costs, timelines, and whether you need a lawyer. The goal is to give you a clear, practical roadmap—written for real people and optimized for search engines.
What Is an Adversary Proceeding in Bankruptcy?
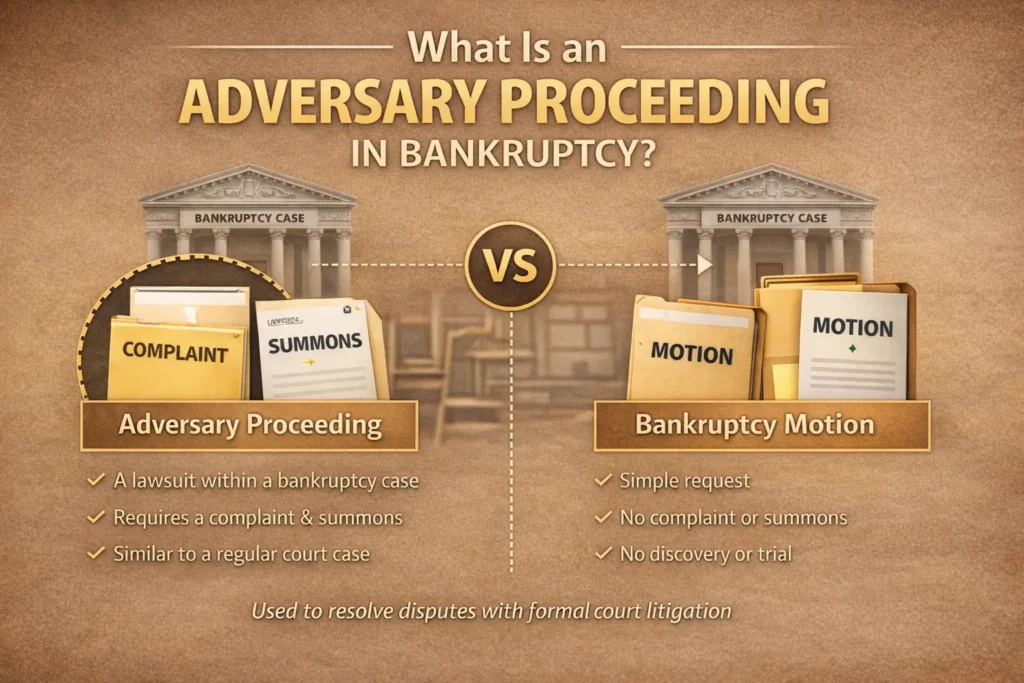
An adversary proceeding in bankruptcy is a lawsuit filed within an existing bankruptcy case. Unlike a standard bankruptcy motion, it follows formal litigation rules similar to civil court cases.
In simple terms:
- Your bankruptcy case is the main case
- An adversary proceeding is a separate lawsuit within that case
It allows the court to resolve serious legal disputes that require:
- Evidence
- Witnesses
- Discovery
- Legal arguments
For a detailed legal definition-
👉 Adversary Proceeding Explained
When Do You Need to File an Adversary Proceeding?
You must file an adversary proceeding when bankruptcy rules require a formal lawsuit instead of a motion.
Common Reasons to File an Adversary Proceeding
An adversary proceeding is required when:
- You want to discharge student loans due to undue hardship
- A creditor claims fraud or misrepresentation
- You want to challenge the dischargeability of a debt
- A creditor disputes whether a debt was discharged
- You are seeking to avoid a lien
- A trustee wants to recover transferred property
- There is a dispute over property ownership
👉 Student loan cases often arise after borrowers face aggressive collection efforts. Learn more about how student loans are collected and why bankruptcy disputes arise: the law requires a formal legal process instead of a simple motion.
Adversary Proceeding vs. Bankruptcy Motion

Many people confuse an adversary proceeding with a bankruptcy motion. However, they are not the same.
Key Differences Explained
| Adversary Proceeding | Bankruptcy Motion |
|---|---|
| Separate lawsuit within bankruptcy | Simple court request |
| Requires a complaint and summons | Usually just a motion |
| Follows litigation rules | Faster and less formal |
| Involves discovery and trial | Often decided quickly |
Therefore, if your issue involves fraud, dischargeability, or creditor misconduct, a motion is usually not enough.
When to File an Adversary Proceeding
Knowing when to file an adversary proceeding is crucial. Filing too late can permanently cost you your legal rights.
Situations That Require Immediate Filing
You should file an adversary proceeding when:
- A creditor files an objection to discharge
- You want to discharge student loans due to undue hardship
- Fraud, pretenses, or misconduct is alleged
- A creditor violates the automatic stay
- Property ownership is disputed
In most cases, strict court deadlines apply.
Adversary Proceeding Filing Deadline
The adversary proceeding filing deadline depends on the type of claim.
Common Deadlines to Know
- Objection to discharge: Usually, 60 days after the first creditors’ meeting
- Student loan discharge: No fixed deadline, but earlier filing is better
- Automatic stay violations: As soon as the violation occurs
- Fraud-related claims: Strict and time-sensitive
Missing a deadline often results in automatic dismissal.
Bankruptcy Adversary Proceeding Requirements
Before filing, you must meet specific legal requirements.
What You Need Before Filing
- An active bankruptcy case
- Legal standing in the dispute
- A valid legal basis under bankruptcy law
- Supporting documentation and evidence
- Compliance with bankruptcy procedural rules
Failure to meet these requirements may lead to rejection.
How to File an Adversary Proceeding in Bankruptcy (Step-by-Step)
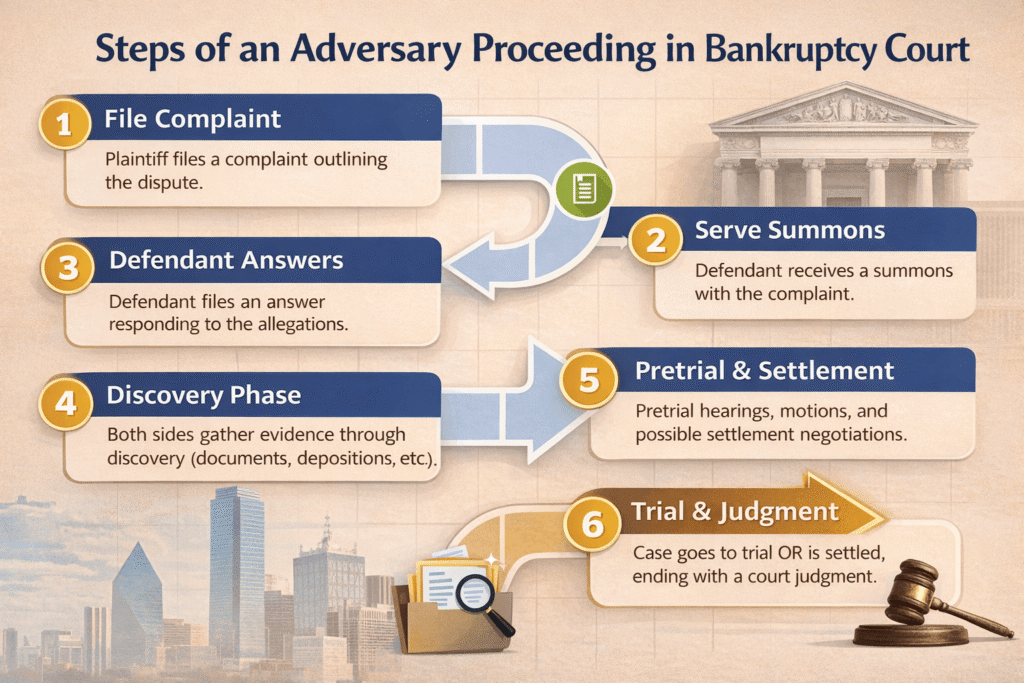
Below is a clear breakdown of the steps for filing an adversary proceeding.
Step 1: Confirm That an Adversary Proceeding Is Required
Before filing, confirm your issue falls under Bankruptcy Rule 7001. Filing the wrong document can result in dismissal and wasted fees.
If you are unsure, review your bankruptcy goals or consult legal guidance—especially for student loan discharge cases.
👉 Read the complete overview of student loan bankruptcy and legal options: enforce legal standards.
Visit for more details – Student Loan Bankruptcy Guide
Step 2: Identify the Correct Parties (Plaintiff and Defendant)
- Plaintiff: Usually the debtor (you), creditor, or trustee
- Defendant: The opposing party (lender, servicer, creditor, trustee)
In student loan cases, defendants often include:
- Federal loan servicers
- Private lenders
- Guaranty agencies
👉 Understanding the difference between federal and private student loans is essential before filing.
Step 3: Draft the Adversary Proceeding Complaint
The adversary’s proceeding complaint is the most critical document in the process.
Your complaint must include:
- Court name and case number
- Parties involved
- Jurisdiction and legal authority
- Factual background
- Legal claims
- Specific relief requested
Common Legal Claims
- Undue hardship (student loans)
- Fraud or false representation
- Willful violation of the bankruptcy stay
- Invalid liens
A poorly written complaint is one of the most common reasons adversary proceedings fail.
Step 4: File the Complaint With the Bankruptcy Court
You file the complaint with the same bankruptcy court handling your main case.
- Filing is usually done electronically (ECF system)
- Pro se filers may file in person or by mail
- Filing fee typically ranges from $350–$400
Once filed, the court assigns:
A summons
A separate adversary case number
Step 5: Serve the Complaint and Summons Properly
Service is not optional—it is mandatory.
You must:
- Serve all defendants
- Follow Bankruptcy Rule 7004
- Meet strict service deadlines
Improper service can result in dismissal, even if your claim is valid.
Step 6: Await the Defendant’s Response
The defendant usually has 30 days to respond.
They may file:
- An answer
- A motion to dismiss
- A motion for summary judgment
Many adversary proceedings are resolved at this stage—without trial.y request a default judgment.
Step 7: Discovery Phase (If Needed)
If the case continues, both sides may exchange:
- Documents
- Interrogatories
- Depositions
Discovery is common in student loan adversary proceedings, especially when proving undue hardship.
Step 8: Settlement, Trial, or Court Decision
Outcomes include:
- Settlement agreement
- Summary judgment
- Trial and judicial ruling
👉 Many private loan cases resolve through negotiation. Learn more about private student loan settlement options
Step 9: Trial and Judgment
If unresolved, the court holds a trial.
The judge will:
- Review evidence
- Hear testimony
- Issue a final judgment
The decision becomes legally binding.
Even small mistakes can lead to dismissal.
Bankruptcy Adversary Proceeding Requirements
To successfully file an adversary proceeding, you must meet several requirements:
- Active bankruptcy case
- Proper jurisdiction
- Correct filing format
- Filing fee payment
- Timely service
- Compliance with deadlines
Failure in any of these areas can derail your case.
Adversary Proceeding Filing Deadline
Deadlines vary by claim type.
Common Deadlines
- Dischargeability complaints: 60 days after the meeting of creditors
- Other actions: May vary by rule and court order
Missing the deadline may permanently bar your claim.
Do I Need a Lawyer to File an Adversary Proceeding?
Legally? No.
Practically? Often, yes.
When You Might File Without a Lawyer
- Simple disputes
- Strong documentation
- Prior legal experience
When a Lawyer Is Strongly Recommended
- Student loan discharge cases
- Fraud allegations
- High-value disputes
- Complex legal arguments
Adversary proceedings involve litigation skills—not just paperwork.
How Long Does an Adversary Proceeding Take?
Timelines vary widely.
Typical Timeframes
- Simple cases: 3–6 months
- Student loan cases: 6–18 months
- Complex litigation: 1–2 years
Settlements can significantly shorten the process.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Filing an Adversary Proceeding
- Filing a motion instead of a complaint
- Missing filing deadlines
- Improper service
- Weak legal arguments
- Inadequate evidence
- Ignoring settlement opportunities
Avoiding these mistakes improves your chances of success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an adversary proceeding in bankruptcy?
A lawsuit filed within a bankruptcy case to resolve disputes requiring formal litigation.
How much does it cost to file an adversary proceeding?
Typically $350–$400, excluding legal fees.
Can I discharge student loans without an adversary proceeding?
No. Student loan discharge requires an adversary proceeding.
Can an adversary proceeding be settled?
Yes. Many cases settle before trial.
Final Thoughts: Is Filing an Adversary Proceeding Worth It?
Filing an adversary proceeding is not easy—but it can be life-changing when done correctly. Whether you are challenging student loans, disputing creditor behavior, or protecting your bankruptcy rights, understanding the process is essential.
If you prepare carefully, meet deadlines, and build a strong legal argument, an adversary proceeding can provide real relief—especially when other options have failed.















Comments (18)
Student Loan Bankruptcy: Discharge, Relief & Legal Options
[…] How to File an Adversary ProceedingStudent Loan Bankruptcy Process Step by Step […]
How Student Loans Are Collected | Federal vs Private Loans
[…] Unpaid student loan debt does not go away and, in most cases, cannot be discharged in bankruptcy. […]
Private Student Loan Settlement Options Explained
[…] Student loan settlement options are strategies that allow borrowers to pay less than the full loan balance by negotiating directly with the lender or a collection agency. […]
Federal vs Private Student Loans: Which One Is Better?
[…] Federal borrowers may explore income-driven repayment, consolidation, or legal relief through filing an adversary proceeding in bankruptcy. […]
Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy for Student Loans
[…] If you are considering suing to discharge student loans, you should first review this detailed guide on how to file an adversary proceeding. […]
Income Driven Repayment vs Bankruptcy: Which Is Better for Student Loans?
[…] A complete legal breakdown is available in this guide onHow to file an adversary proceeding for student loans […]
Is Student Loan Bankruptcy Worth It? Pros, Cons & Real Relief
[…] you want a clear explanation of how this works, this step-by-step guide on👉 How to file an adversary proceedingwalks through the process in plain […]
Student Loan Forgiveness House Vote: Latest Updates
[…] example, many borrowers do not realize that they can challenge student loans in bankruptcy by filing an adversary proceeding, which is often used to seek discharge of student […]
Federal Student Loan Forgiveness Public Service Application
[…] If you are facing legal hardship, read this step-by-step guide on how to file an adversary proceeding to challenge student loans in bankruptcy […]
Medical Hardship Student Loan Relief: Eligibility & Options
[…] 👉 How to file an adversary proceeding […]
Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment? Explained
[…] most cases, this requires filing an adversary proceeding.Borrowers should first understand how to file an adversary proceeding before pursuing […]
Student Loan Deferment Guide 2026: Eligibility, Hardship & Steps
[…] loans can be discharged through an adversary proceeding.👉 How to file an adversary proceeding👉 Student loan bankruptcy complete […]
What Is a Student Loan? A Complete 2026 Guide for Borrowers - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] However, when repayment becomes overwhelming, many borrowers look at legal options such as filing an adversary proceeding for student loan bankruptcy to seek discharge due to financial hardship. This legal process is explained here:👉 https://federalstudentloandebt.com/how-to-file-an-adversary-proceeding/ […]
What Is a Student Loan? Full Guide to Types, Rates & Repayment
[…] However, when repayment becomes overwhelming, many borrowers look at legal options such as filing an adversary proceeding for student loan bankruptcy to seek discharge due to financial hardship. This legal process is explained here:👉 https://federalstudentloandebt.com/how-to-file-an-adversary-proceeding/ […]
Student Loan Payment Plan: Complete Guide to Repayment Options, Forgiveness, Interest, and Strategies (2026 Update) - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] Student loan repayment is complicated, which is why many borrowers also explore legal protections such as filing an adversary proceeding for student loan bankruptcy if repayment becomes impossible.Learn more here:👉 How to file an adversary proceeding for student loan bankruptcyhttps://federalstudentloandebt.com/how-to-file-an-adversary-proceeding/ […]
Student Loan Forgiveness Programs: Eligibility, Types & Relief Guide
[…] Detailed guide on how to file:👉 How to File an Adversary Proceeding for Student Loan Bankruptcy […]
Student Loan Debt Help: Relief, Forgiveness & Repayment Options Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] Learn how to file it here:👉 How to file an adversary proceeding for student loan bankruptcy […]
Is Student Loan Bankruptcy Worth It? - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] You can see a full detailed breakdown inside:✔ How to file an adversary proceeding […]