
Understanding how student loans are collected is critical for borrowers who want to avoid default, protect their income, and make informed financial decisions. Student loan collection follows a structured legal process that differs significantly depending on whether the loan is federal or private.
Before diving into collections, it’s essential to understand what student loans are and how the system works overall.
➡️ Student Loans Explained: Definition, Types, and Legal Framework
This complete guide explains how student loans are collected, what happens if you don’t pay, when loans go to collections, and how to stop student loan collections before serious financial consequences occur.
1. What Does Student Loan Collection Mean?
Student loan collection refers to the legal and administrative actions taken by lenders or government agencies to recover unpaid student loan debt. When a borrower misses payments for an extended period, the loan becomes delinquent and may eventually enter default.
Once a loan is in default, collectors may:
- Contact you repeatedly
- Garnish wages
- Seize tax refunds
- Add collection fees
- File lawsuits (especially for private loans)
Understanding this process early can help prevent long-term financial damage. Financial damage.
2. How Are Student Loans Collected?
Student loans are collected through a progressive system, starting with reminders and escalating to forced collection measures if payments remain unpaid.
In general, student loans are collected through:
- Billing statements and late notices
- Phone calls, emails, and letters
- Assignment to a collection agency
- Administrative enforcement (federal loans)
- Court judgments (private loans)
The collection method depends heavily on whether the loan is federal or private.
➡️ Federal vs. Private Student Loans: How Collection Rules Differ
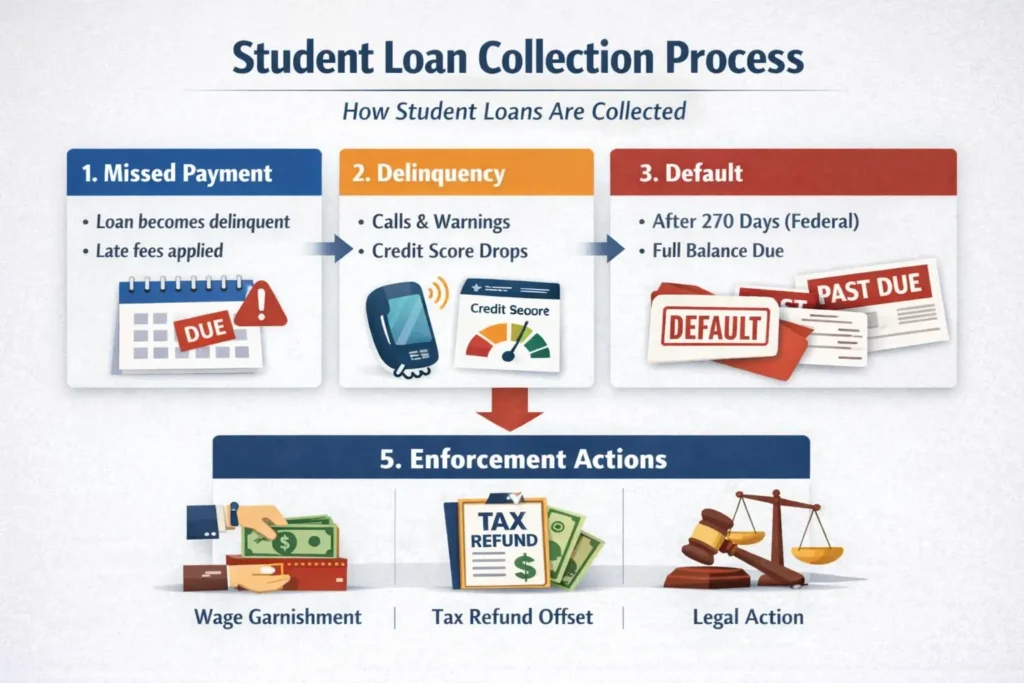
3. The Student Loan Collection Process (Step by Step)
Understanding the student loan collection process step by step helps borrowers anticipate what happens next.
Step 1: Missed Payment (Delinquency Begins)
- Delinquency starts the day after a missed payment
- Late fees may apply
- Credit score impact may occur after 30–90 days
Step 2: Continued Delinquency
- Lenders begin phone calls and written notices
- Credit bureaus are notified
- Interest continues to accrue
Step 3: Default
- Federal loans default after 270 days
- Private loans may default after 90–180 days
- The entire loan balance becomes due immediately
Step 4: Student Loan Collections
- Account is transferred to collections
- Collection fees may be added
- Aggressive recovery efforts begin
Step 5: Enforcement Actions
- Wage garnishment
- Tax refund offset
- Lawsuits (private loans)
4. What Happens If You Don’t Pay Student Loans?
What happens if you don’t pay student loans?
Failing to pay student loans can lead to serious financial and legal consequences, including:
- Loan default
- Credit score damage
- Loss of eligibility for deferment or forgiveness
- Wage garnishment
- Tax refund seizure
- Lawsuits (private loans)
Unpaid student loan debt does not go away and, in most cases, cannot be discharged in bankruptcy.
5. When Do Student Loans Go to Collections?
When do student loans go to collections?
The timeline varies by loan type:
| Loan Type | Time Before Collections |
| Federal student loans | After 270 days of non-payment |
| Private student loans | 90–180 days (varies by lender) |
Once loans go to collections:
- Additional fees are added.
- Collection agencies are authorized to recover the debt.
- Borrowers lose many repayment options.

6. Federal Student Loan Collections Explained
Federal student loan collections are managed under U.S. Government regulations and are more potent than private collections.
Key Features of Federal Student Loan Collections
- No court order required for wage garnishment
- Tax refunds can be seized.
- Social Security benefits may be offset.
- Collection fees can be substantial.
Federal Collection Methods Include:
- Treasury Offset Program (TOP)
- Administrative Wage Garnishment (AWG)
- Assignment to private collection agencies
Despite their power, federal loans offer more relief options than private loans.
7. Private Student Loan Collections Explained
State laws and loan contracts govern private student loan collections.
How Private Collections Work
- Lenders must file a lawsuit to garnish wages
- A court judgment is required
- Collection agencies act on the lender’s behalf
- Settlements are often negotiable
Because of this flexibility, many borrowers explore settlement once private loans enter collections.
➡️ Private Student Loan Settlement Options: How Borrowers Reduce Debt
8. Wage Garnishment for Student Loans
Wage garnishment for student loans explained.
Wage garnishment allows lenders to take a portion of your paycheck to repay student loan debt.
Federal Student Loans:
- Up to 15% of disposable income
- No court order required
- Employer must comply
Private Student Loans:
- Court judgment required
- Garnishment limits vary by state.
- Legal defenses may apply.
Wage garnishment continues until:
- The debt is paid
- A settlement is reached.
- Rehabilitation or consolidation is completed (federal loans)
9. Tax Refund Offset and Student Loans
Tax refund offsets student loans.
Federal student loan collectors can intercept your federal tax refund through the Treasury Offset Program.
What Can Be Taken:
- Federal tax refunds
- State tax refunds (in some cases)
- Certain federal benefits
Important Notes:
- Borrowers receive advance notice.
- Offsets continue annually until resolved.
- Filing jointly may put the spouse’s refund at risk.
Private lenders cannot seize tax refunds without a court judgment.
10. Student Loan Default Consequences
Student loan default consequences include:
- Immediate full balance due
- Severe credit damage
- Loss of deferment and forbearance
- Ineligibility for forgiveness programs
- Increased interest and collection fees
- Difficulty renting housing or obtaining loans
Defaulted student loans can affect:
- Employment background checks
- Professional licenses
- Security clearances
11. How to Stop Student Loan Collections Legally
Stopping student loan collections is possible—especially for federal loans.
Options for Federal Student Loans
- Loan Rehabilitation – nine affordable payments
- Loan Consolidation – faster exit from default
- Income-Driven Repayment Plans
- Hardship Deferment or Forbearance
Options for Private Student Loans
- Negotiate a settlement
- Request hardship assistance
- Refinance (if eligible)
- Hire a student loan attorney
- Challenge improper collections
If collections escalate into legal disputes, some borrowers explore bankruptcy-related remedies.
➡️ Student Loan Bankruptcy: Discharge, Relief, and Legal Options
In some instances, borrowers must file a lawsuit within bankruptcy court.
➡️ How to File an Adversary Proceeding in Bankruptcy
⚠️ Avoid debt relief scams promising instant forgiveness.

12. Frequently Asked Questions
How long does student loan collection last?
Federal student loan collections can last indefinitely until resolved. Private loans depend on court judgments and state laws.
Can student loans be forgiven after collections?
Yes, federal loans may qualify for forgiveness after rehabilitation or consolidation under specific programs.
Can collectors take all my paycheck?
No. Federal garnishment is capped at 15%. Private garnishment limits vary by state.
Do student loans ever expire?
Federal student loans do not expire. Statutes of limitation may limit private loans.
Understanding how student loans are collected empowers borrowers to act early and protect their financial future. Whether dealing with federal or private student loan collections, knowing your rights and options is essential.















Comments (21)
Student Loan Bankruptcy: Discharge, Relief & Legal Options
[…] How Student Loans Are Collected […]
Private Student Loan Settlement Options Explained
[…] Private Student Loan Debt Settlement (via companies) […]
Federal vs Private Student Loans: Which One Is Better?
[…] This difference alone explains why federal loans are generally safer for students. […]
How to File an Adversary Proceeding in Bankruptcy Court
[…] you may need to file an adversary proceeding. For example, this applies when you want to discharge student loans, challenge creditor fraud, or stop a […]
Can Bankruptcy Stop Student Loan Garnishment? Explained
[…] Before looking at bankruptcy relief, it helps to understand how student loans are collected. […]
Student Loan Relief Due to Illness: Medical Hardship Options
[…] 👉 how student loans are collected […]
Is Student Loan Bankruptcy Worth It? Pros, Cons & Real Relief
[…] you are unsure how enforcement works, understanding👉 How student loans are collectedIt is essential, because collection activity often determines whether bankruptcy becomes […]
Income Driven Repayment vs Bankruptcy: Which Is Better for Student Loans?
[…] This enforcement process is explained step by step inHow student loans are collected […]
Chapter 7 vs Chapter 13 Bankruptcy for Student Loans
[…] better understand enforcement risks, it is also important to know how student loans are collected and what actions lenders can […]
Student Loan Bankruptcy Process Step by Step
[…] ➡️ How Student Loans Are Collected: From Missed Payments to Lawsuits […]
Federal Student Loan Forgiveness Public Service Application
[…] Learn how student loans are collected and how enforcement actions begin […]
Student Loan Forgiveness for Teachers
[…] 👉 How student loans are collected […]
Student Loan Refinance: How It Works, Best Lenders
[…] How student loans are collected👉 Student loan […]
Student Loan Social Security Garnishment: How It Works
[…] If you’re unsure about how collections work, here is a helpful guide:👉 How Student Loans Are Collected […]
Student Loan Consolidation Guide 2026
[…] If your FFEL loans are in collections, read how collections work:👉 How student loans are collected […]
Student Loan Forgiveness House Vote: Latest Updates
[…] already facing collections should immediately learn how student loans are collected, since wage garnishment, tax refund offsets, and lawsuits can begin long before any forgiveness […]
Student Loan Debt Help: Relief, Forgiveness & Repayment Options Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] Understanding collections is essential:👉 How student loans are collectedhttps://federalstudentloandebt.com/student-loans-are-collected/ […]
Student Loan Forgiveness Programs: Eligibility, Types & Relief Guide
[…] To understand the collections process, see:👉 How Student Loans Are Collected […]
Student Loan Payment Plan: Complete Guide to Repayment Options, Forgiveness, Interest, and Strategies - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] If repayment becomes difficult and you miss payments, it is important to understand:👉 How student loans are collected […]
What Is a Student Loan? Full Guide to Types, Rates & Repayment
[…] how student loans are collected in […]
Is Student Loan Bankruptcy Worth It? - Las Vegas Student Loan Lawyer | Federal Student Loan Debt Relief
[…] To understand how this pressure builds, read:✔ how student loans are collected […]